Rejuva Aesthetica Plastic Surgery Clinic in Ahmedabad

Menu
Co2 Laser Treatment
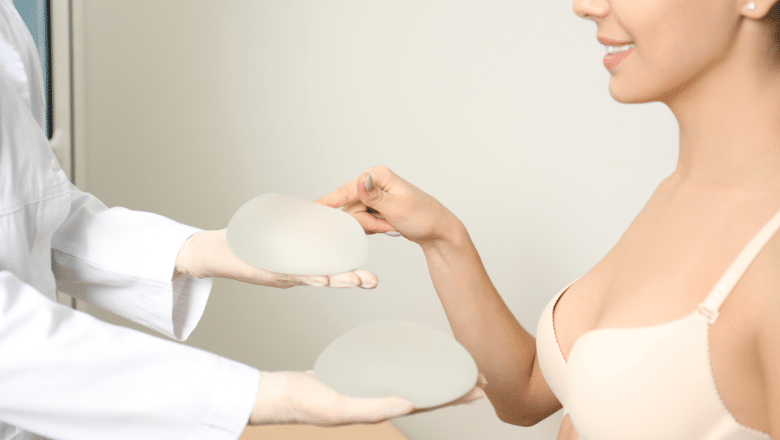
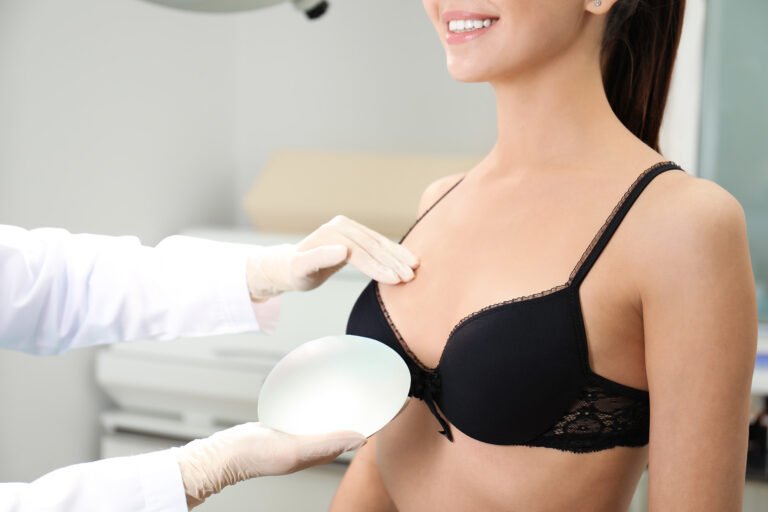

Breast implant treatment, commonly referred to as breast augmentation or augmentation mammoplasty, is a surgical procedure designed to enhance the size and shape of a woman’s breasts. This treatment can be performed for various reasons, including cosmetic enhancement, reconstruction after mastectomy, or correcting breast asymmetry.
How Breast Implant Surgery Works
The process typically involves the following steps:- Consultation: A thorough consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon is essential to discuss goals, expectations, and the types of implants available (saline or silicone).
- Anesthesia: The procedure usually requires general anesthesia, although local anesthesia may be used in some cases.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision in one of several discreet locations:
- Inframammary: Under the breast fold.
- Periareolar: Around the nipple.
- Transaxillary: Under the arm.
- Umbilical: Through the belly button (less common).
- Implant Placement: The implant is inserted into a pocket created either:
- Submuscular: Under the chest muscle.
- Subglandular: Above the chest muscle but beneath the breast tissue.
- Closure: The incisions are closed using sutures, skin adhesive, or surgical tape.
Types of Breast Implants
Breast implants come in two main types:- Saline Implants: These are filled with sterile salt water and can be adjusted for size during surgery.
- Silicone Implants: Pre-filled with silicone gel, these implants tend to feel more like natural breast tissue.
Benefits of Breast Implant Treatment
Breast implant treatment offers several advantages:- Enhanced Appearance: Many women report increased self-confidence and body image satisfaction following breast augmentation.
- Reconstruction Options: It provides options for women undergoing reconstruction after mastectomy or injury.
- Customizable Results: Patients can choose from various sizes and shapes to achieve their desired look.
Risks and Considerations
While breast augmentation is generally safe, potential risks include:- Surgical Complications: Infections, bleeding, or adverse reactions to anesthesia.
- Capsular Contracture: A condition where scar tissue forms around the implant, potentially causing discomfort or changes in appearance.
- Implant Rupture or Leakage: Particularly with saline implants, which may deflate if damaged.
Recovery Process
Post-operative recovery typically involves:- Soreness and swelling for a few weeks.
- Wearing a supportive bra for comfort and support during healing.
- Gradual return to normal activities within a few weeks, with full recovery taking about six to eight weeks.
Conclusion
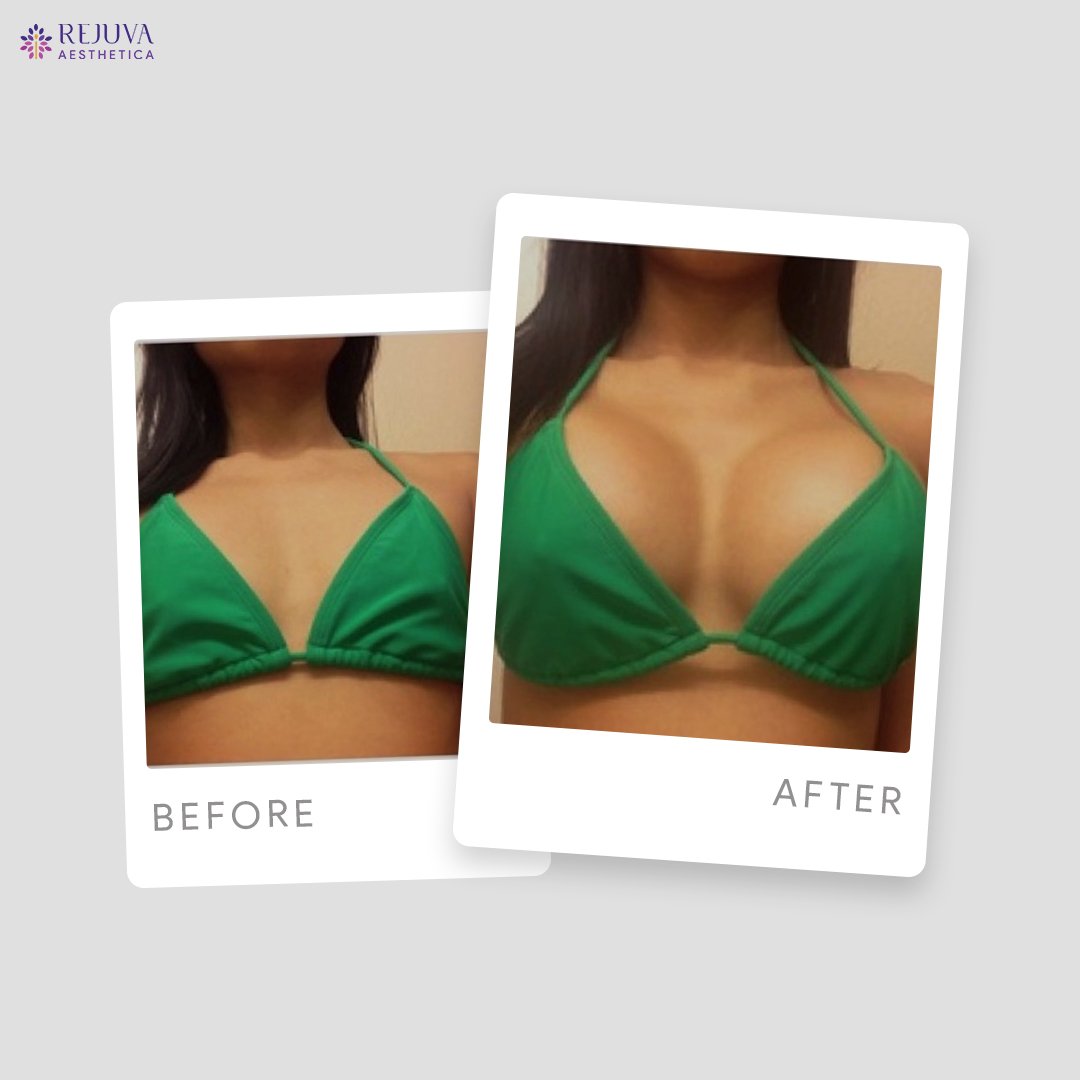
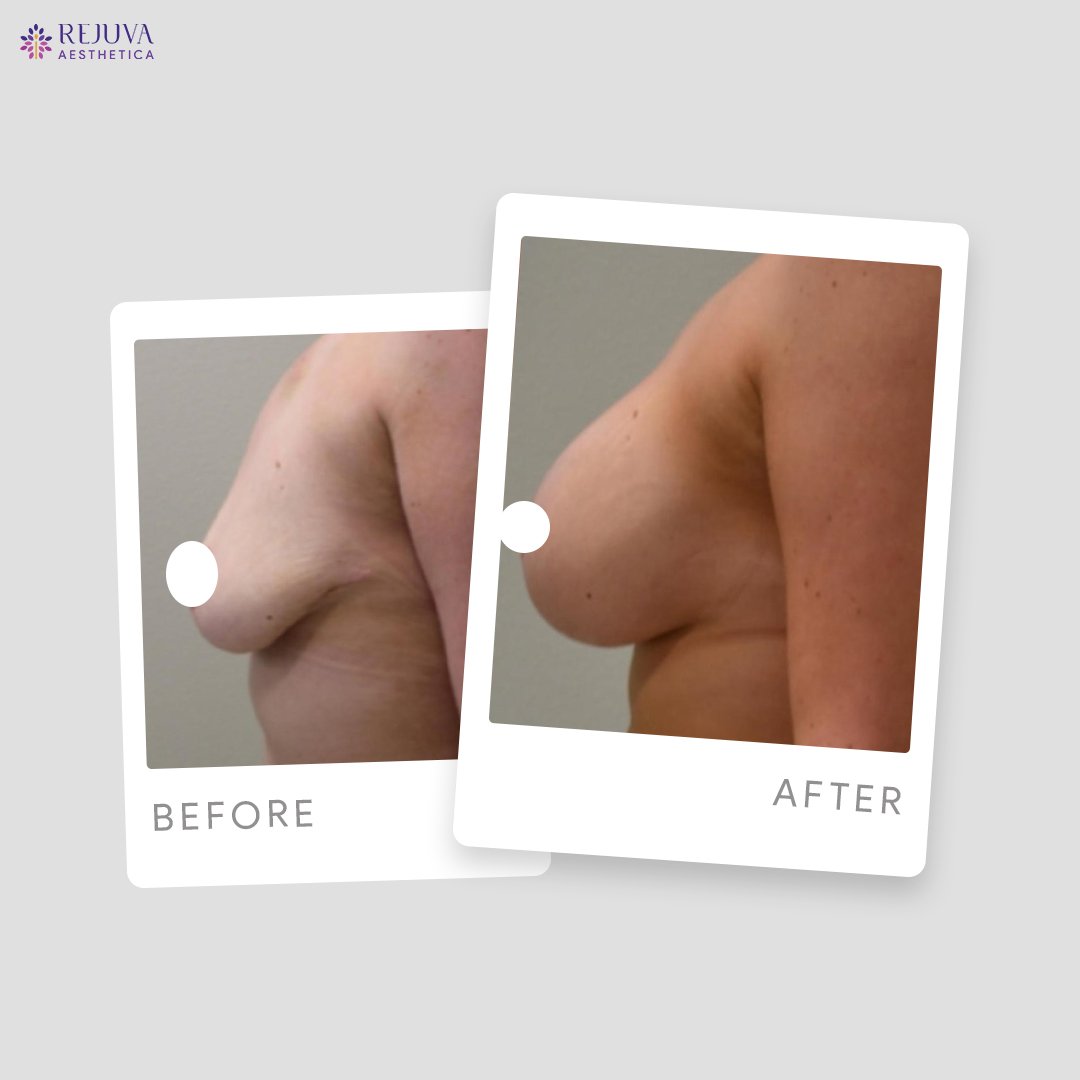
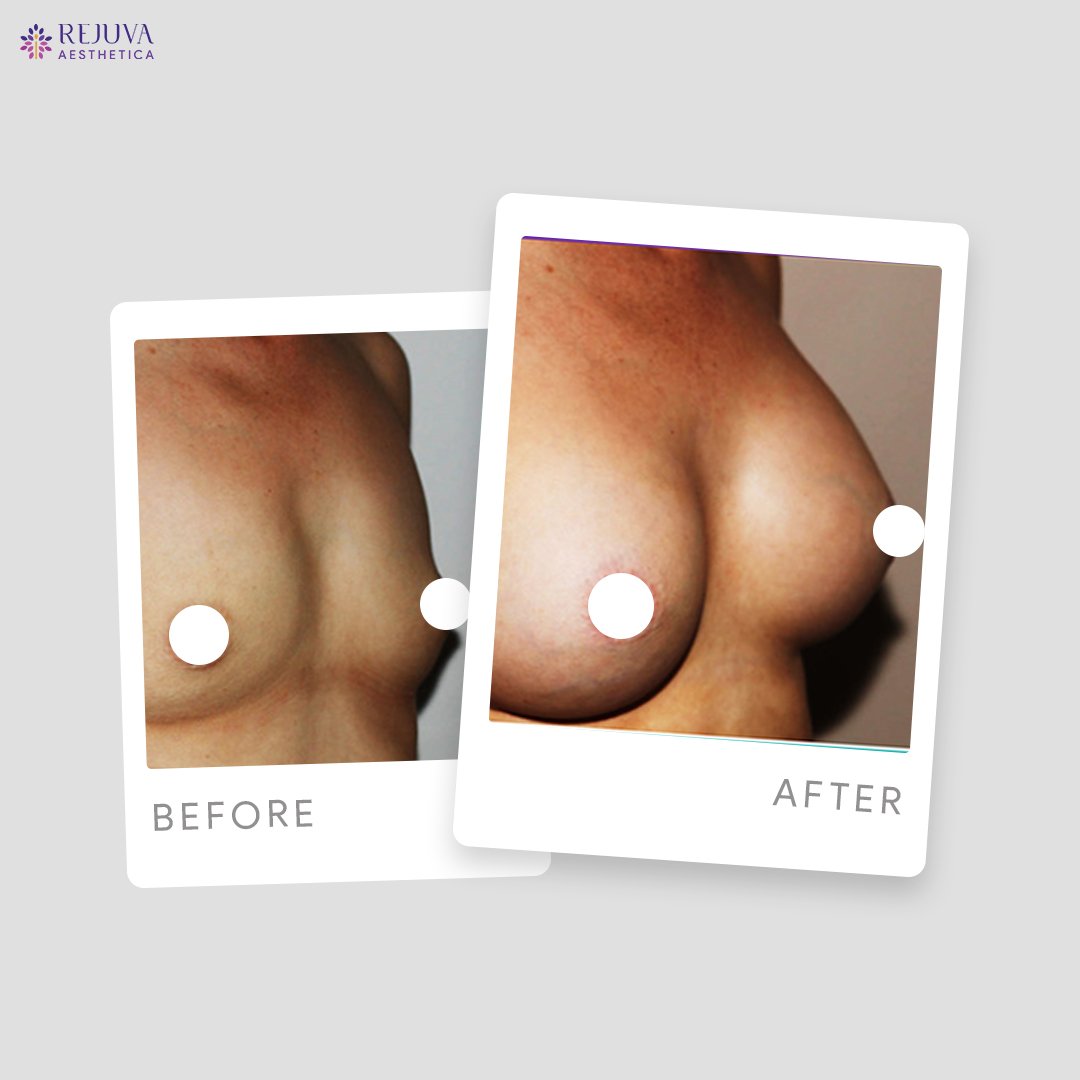
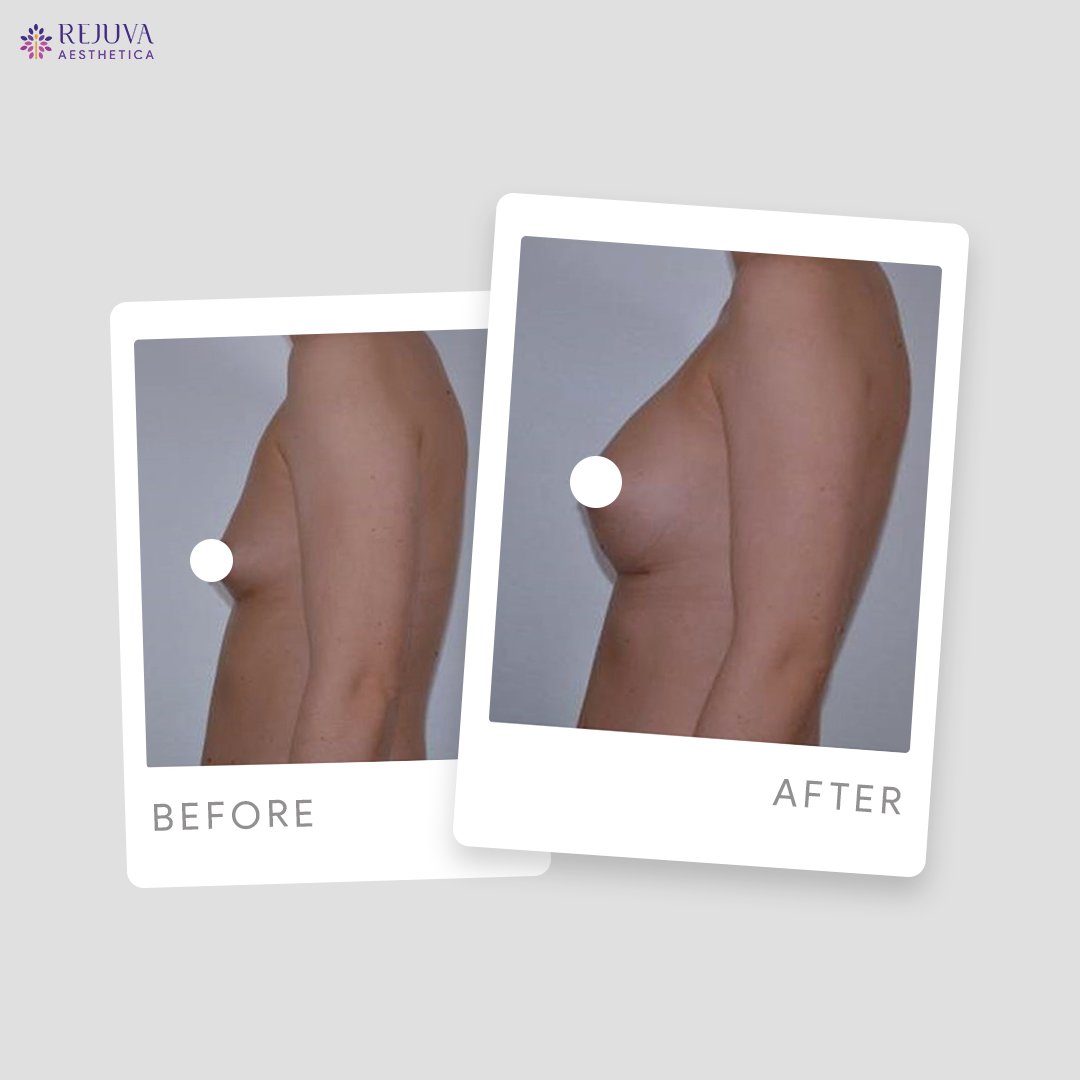
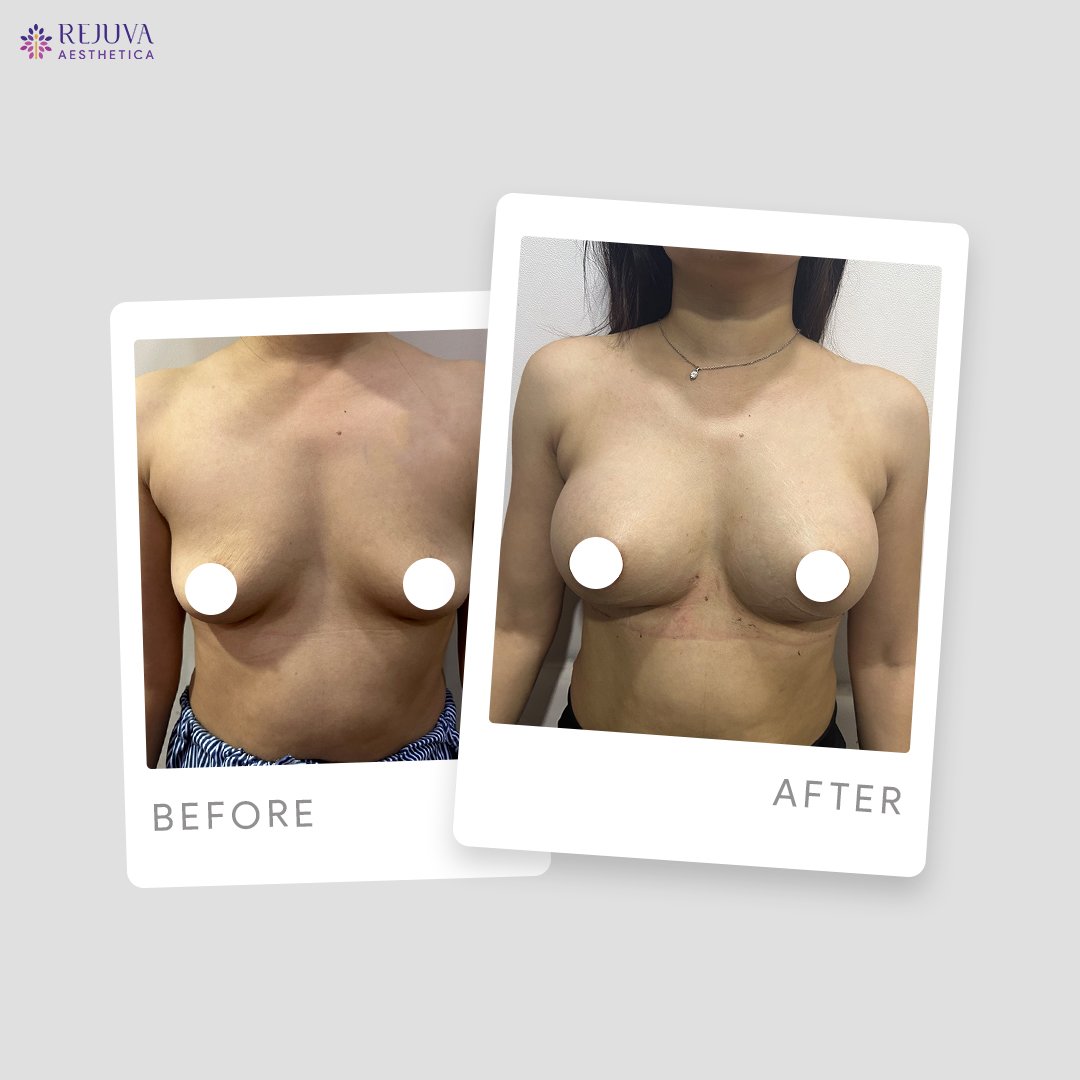
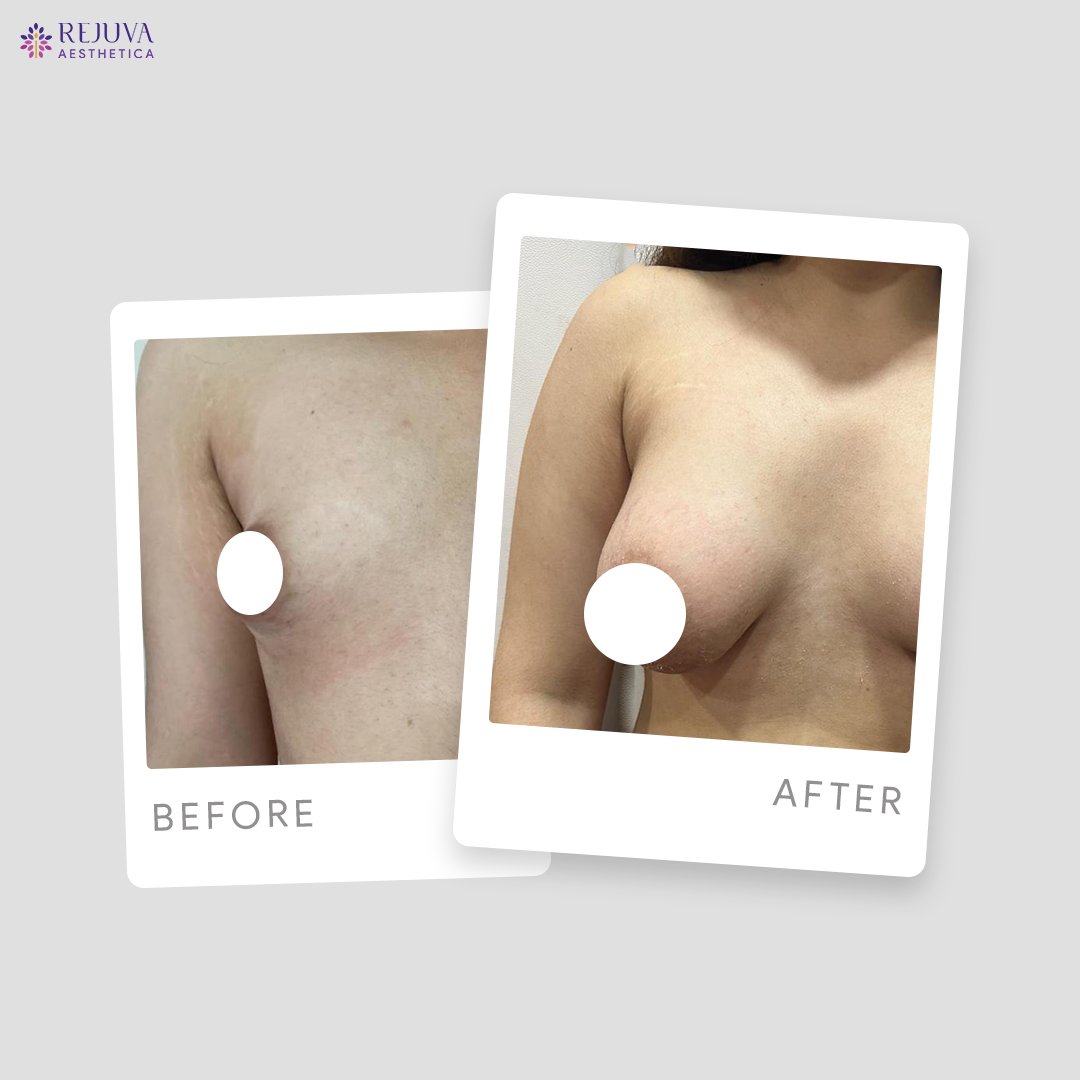
Breast implant treatment is a widely sought-after procedure that can significantly enhance a woman’s figure and boost self-esteem. With various options available and advancements in surgical techniques, it remains a popular choice for both cosmetic and reconstructive purposes.For those considering breast augmentation, consulting with an experienced plastic surgeon is crucial to ensure personalized care and optimal outcomes.Before and After Treatment